 Longboards & Health Research
Longboards & Health Research
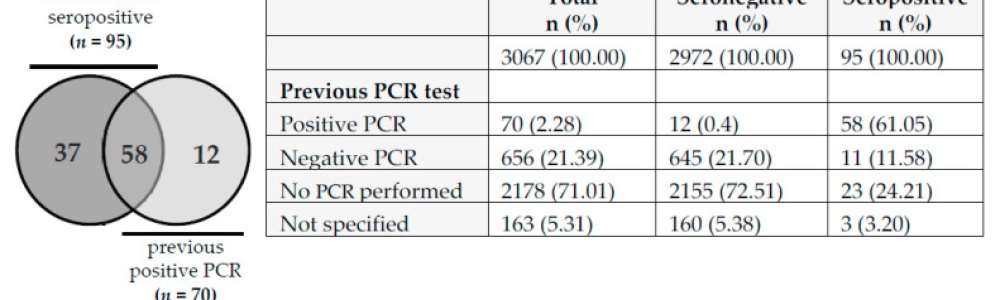
Assessment of SARS-CoV-2 Infection among Healthcare Workers
Larribère L, Gordejeva J, Kuhnhenn L, Kurscheidt M, Pobiruchin M, Vladimirova D, Martin M, Roser M, Schramm W, Martens UM, Eigenbrod T. Assessment of SARS-CoV-2 Infection among Healthcare Workers of a German COVID-19 Treatment Center. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Jul 1;18(13):7057. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18137057. PMID: 34281000; PMCID: PMC8297119.
Abstract
To date, more than 160 million people have been infected with COVID-19 worldwide. In the present study, we investigated the history of SARS-CoV-2 infection among 3067 healthcare workers (HCW) in a German COVID-19 treatment center during the early phase of the pandemic (July 2020) based on the seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies and self-reported previous PCR results. The results demonstrate a low prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 infection (n = 107 [3.5%]) with no increased risk for employees with a high level of patient exposure in general or working in COVID-19-confined areas in particular. This suggests that the local hygiene standards implemented in our hospital during the first wave of COVID-19 pandemic were effective in preventing patient-to-HCW transmission. No evidence for highly mobile staff serving as a vector for SARS-CoV-2 transmission could be found. In addition, impairment of smell and/or taste was strongly associated with SARS-CoV-2 history.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; epidemiology; health care workers; infection risk; infectious disease; transmission.